Contents
It is known that the maximum running length for Ethernet cables is 100 meters (328 feet), but in many situations, this distance is not enough for cable installation needs. So, what can you do to extend the network connectivity beyond 100 meters? The media converter provides the solution by converting signals between copper cables and fiber optic cables for extended Ethernet transmission.
What is a media converter and how does it work? What are the different types of media converters? This article will give clear answers to these questions.
What is Media Converter?
The media converter, also known as the fiber media converter or Ethernet to fiber media converter, is a flexible solution that functions as the transceiver that usually converts the signal from one type of medium into a suitable format for the transmission of another medium. A media converter usually converts the electrical signals in the twisted pair cables to light pulses for fiber optic cabling without signal loss or degradation.
A typical media converter features more than two optical ports for transmitting and receiving optical signals. The media converter is a convenient and cost-effective solution to optimizing the fiber optic network connection if the distance between two network devices is longer than the maximum running length of copper cables.

Media Converter Types
Media converters can be divided into many types according to different requirements.
Based on Different Styles
- Chassis Media Converters: The chassis media converter can be installed in a lot of chassis configurations. It contains many independent media converters and is designed for high-density data centers. The chassis media converter can handle different types of cables, widely used in LAN wiring closets, data converters, and switching rooms.
- Slide-in Media Converter Cards: The slide-in media converter gets its name because it can be slid into the chassis. It provides various ports for large network requirements and offers added flexibility and convenience for network maintenance.
- Standalone Media Converters: Media converters also come in standalone type for tight places, so these converters feature a compact size. They are also easy to install and often used in telecommunication cabinets and boxes.

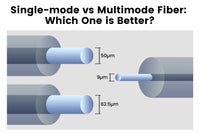
Single-mode vs. Multimode Media Converter
Optical fibers are classified into single-mode and multimode types. Consequently, media converters are also available in single-mode and multimode types to meet different fiber needs.
- Single-mode Media Converter: The single-mode media converter uses a transverse mode that can only transmit signals in a single direction. With a small-diameter core of 9 microns to 5 microns, the single-mode media converter causes a low signal loss.
- Multimode Media Converter: The multimode media converter allows for two or more. transmission directions. But with a larger core diameter of 50 microns to 5microns, the multimode media converter has high light dispersion and authentication rates.
Based on Different Conversions
- Fiber-to-fiber Media Converter: Fiber-to-fiber media converter provides a connection between multi-mode and single-mode fibers or between single-fiber and dual-fiber. The fiber-to-fiber converter converts a wavelength to another wavelength, which is widely used in TDM and Ethernet.
- Copper-to-fiber Media Converter:With RJ45 ports for electrical signals and fiber ports for optical signals, copper-to-fiber converters offer connectivity for different Ethernet devices. These media converters support Ethernet, Fast Ethernet, and 10 Gbps Ethernet based on IEEE 802.3 standard.
PoE vs. Non-PoE Media Converter
Compared to non-PoE media converters, PoE media converters provide data and power by a single Ethernet cable. They can power devices, such as IP phones, IP cameras, and video meeting equipment.
Managed vs. Unmanaged Media Converter
- Unmanaged Media Converter:The unmanaged media converter can easily allow for communication between two systems or protocols. They feature a plug-and-play design and are easy to use for novices and DIYers.
- Managed Media Converter:Managed media converters can be more expensive than unmanaged ones as they can provide remote management, fault detection, and system monitoring. Better management, security, and reliability make them a prior choice for large data centers and enterprise networks.
Commercial vs. Industrial Media Converter
Commercial media converters are suitable for indoor environments with stable temperatures. They are commonly used for data center or office applications. Industrial media converters are suitable for bad environments. For example, it can withstand temperatures between -40 °C and 85 °C. So they are perfect for industrial networks.
Benefits of Media Converters
Media converters provide an efficient solution to network installation at high speed and over long distances. These devices play a crucial role in creating a reliable and stable network. Learn more about the benefits of media converters in the following content.
Larger Network Range: The media converter allows for a larger network range as it uses fiber optic cables. It is suitable for connecting devices that are far away from the network switch.
Cost-effectiveness: By using the media converter, people can easily solve the interconnection problem among various networks instead of changing the network infrastructure or installing new cables.
Enhanced Security: Compared to traditional copper cables, fiber optic cables are immune to electromagnetic interference. So, the fiber media converter provides enhanced security for signal transmission and ensures optimal network performance.
Higher Speed: The media converter can help convert signal speed during conversion in different transmission media. For example, media converters support transmitting speeds from 10 Mbps to 100 Mbps or from 100 Mbps to 1000 Mbps.
Flexibility: The media converter can convert signals from one media to various network media. For example, you can connect copper to fiber, or single-mode fiber to multimode fiber.
Future-proofing: The media converter can support different network technologies to ensure the reliability and stability of the network. It can future proof your network.
Applications of Media Converter
Media converters have a wide range of applications in modern life. The media converters can be used for computers, switches, routers, printers, and other devices, facilitating an intelligent and effective working environment. In industry, media converters are used for PLCs, sensors, and robots which improves industrial automatic level. Media converters are also used in medical imaging devices like MRI machines and CAT scans. Besides, they also play an important role in security systems. For example, PoE media converters are widely used for IP security cameras, controllers, and sensors.
Conclusion
The media converter provides an easy and efficient solution to various network connections. They are available in different types to meet specific needs. If you are new to a media converter, choosing the right one may be difficult, and you should consider factors like distance, fiber type, connector type, data rate, and power option.
For more information on this topic, you can keep up on our blogs. While VCELINK offers general and basic information for our customers and other visitors to the website, it’s not professional advice.





Be the first one to comment.
Leave a comment