Contents
Like privacy’s importance to every person, copyright also means a lot to books and movies. Copyright infringement also happens in the digital and HDCP was created to help combat this challenge. With the surge in copyright violations, the industry faces substantial losses.
Fortunately, HDCP (High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection) has emerged as a pivotal technology in preventing content piracy. Since its inception, HDCP has played a crucial role in preserving the integrity of digital content. While HDCP may be unfamiliar to some, its impact on daily life is profound, especially for TV programs or movies.
We’ll further explore how HDCP works to protect media properties in the following content.
What is HDCP?
High Digital Content Protection, short for HDCP, was created by Intel Corporation. HDCP is an encryption algorithm to protect audio and video from unauthorized copies. HDCP can protect data transmitted by DisplayPort (DP), Digital Visual Interface (DVI), High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI), Gigabit Video Interface (GVIF), Unified Display Interface (UDI), etc.
HDCP can effectively protect the audio and video signals during their journey from source devices like Blu-ray discs or cable boxes to display devices, such as monitors or smart TVs. However, it's crucial to note that not all devices and media support HDCP. To ensure HDCP compliance, devices or cables must meet the specifications and standards outlined by Digital Content Protection to obtain the license. Using non-compliant transmitters, receivers, splitters, or cables will result in HDCP-incompatible audio and video. This can pose a challenge when accessing content from HDCP-protected sources such as Disney and Netflix.
Another important aspect to note about HDCP is its reliance on cable connections. HDCP protection is only applicable when devices are connected via cables. If you stream content directly through built-in apps, HDCP won’t work.
Note: Some people may be confused about HDCP and HDMI. But in fact, they are two different technologies. HDCP is a protocol protecting digital content copyright during digital transmission. Whereas HDMI is a physical cable for transmitting digital data including audio and video. HDCP is software-related while HDMI is hardware-related. HDMI cables generally support HDCP to connect two HDCP-compliant devices.
How Does HDCP Work?
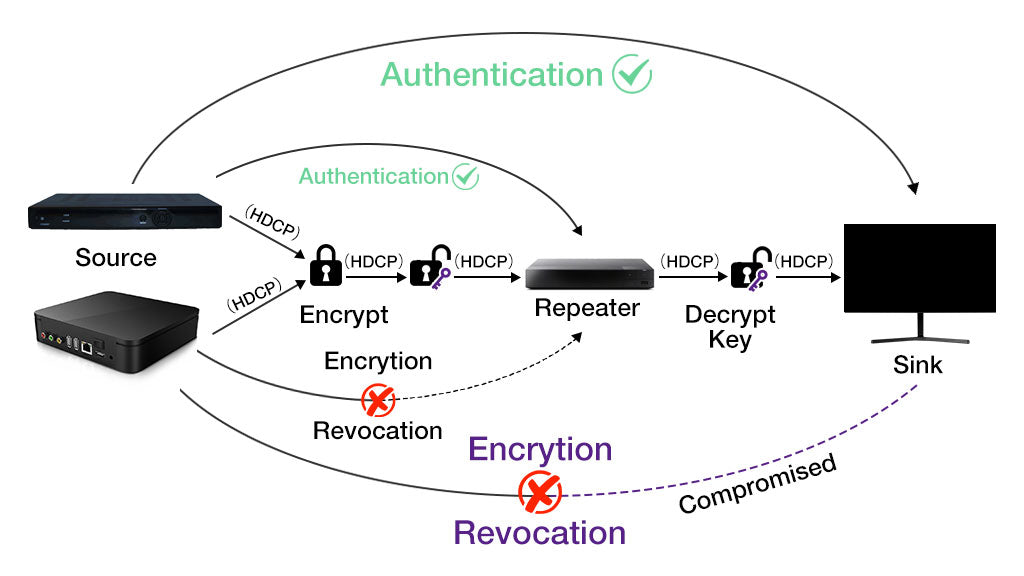
HDCP creates a secure connection between the input and output devices by a handshake system. HDCP encrypts the digital content from the source device. Each HDCP devices have a unique 56-bit private key and a 40-bit vector known as Key Selection Vector (KSV). Before transmitting, the source devices and receivers exchange KSVs, known as an authentication process, to ensure that the receiver is authorized to receive the data. If it is successful, the encrypted connection will be created the data stream will be decrypted and displayed on the screen. There are three main processes during the work:
Authentication: The process confirms whether the source device and receiver device are authorized or not. The authorized devices will exchange their encryption keys with each other, so they are allowed to get the shared encryption keys for transmitting the signal.
Revocation: It can detect if devices are compromised. If the receiver device is deemed compromised, HDCP will revoke the permission to transmit or receive content.
Encryption: The signal is encrypted before being transmitted to the sink via cables. It is designed to prevent piracy and keep the data stream secure.
HDCP Versions
Over the years, HDCP has evolved from HDCP 1.0 to HDCP 2.3. Initially, HDCP 1.0 only supported DVI connections. However, as HDCP progressed, it began to encompass a wider range of connections, including DP, HDMI, GVIF, and UDI.
HDCP 1.4 and HDCP 2.2 have been widely used nowadays. HDCP 1.4 was designed for full HD while HDCP 2.2 was developed to support ultra 4K media. To enjoy 4K video seamlessly, all devices within the system must support HDCP 2.2.
The latest version, HDCP 2.3, adopts the new encryption and decryption algorithms. Compared to HDCP 2.2, 2.3 supports 8K resolution and maintains backward-compatible. However, compatibility issues may arise if devices are not updated to support the latest HDCP version.
HDCP Device Types
Only HDCP-compatible devices can transmit the signal protected by HDCP. The devices are divided into three types: sources, sinks, and repeaters.
- Source:The source device sends the content. Common source devices include DVD players, Blu-Ray players, streaming boxes, and gaming consoles.
- Sink: The device receives the content and displays it on the screen. The sink or transmitter includes TVs, digital projectors, monitors, etc.
-
Repeater: The repeater usually has both inputs and outputs. It accepts content and retransmits the data. For example, splitters, switchers, and audio-video receivers are typical repeater devices.

HDCP Errors
HDCP Errors may happen when you use Apple TV, Netflix, Roku TV, Chromecast, or other platforms and devices. Your display might show messages like “HDCP ERROR” and “ERROR: NON-HDCP OUTPUT”. However, this doesn't necessarily indicate that you're playing unprotected content. HDCP errors can occur due to various factors.
What Causes HDCP Errors?
Several factors can lead to HDCP errors. Let's explore some common reasons:
- Out-dated TVs or Displays: If your HDTV or display was manufactured before the version of HDCP you're using, an HDCP Error may occur due to non-compliance of the HDMI port with HDCP standards.
- Handshaking Issues: Ifthe handshake error occurs, you’ll also get an HDCP error. This often indicates the interface problem.
- Incompatible Devices: If you use devices or cables without HDCP compliance, HDCP errors can also happen.
How to Solve HDCP Errors?
HDCP errors can affect your viewing experience, read on to learn some solutions:
- Restart Devices
Restarting is often an effective solution for technical issues. By rebooting your devices, you can establish the connection again.
- Check Connection
Loose connections can often cause HDCP errors, so ensure that your cables and ports are securely connected.
- Replace Hardware
Incompatible cables or devices will lead to HDCP Errors. Before wiring, you should ensure your cables are HDCP-compliant including devices like HDMI extenders, splitters, switches, etc. If you find your cables or devices cannot support HDCP, go for a new one.
- Install an HDMI Splitter
Try to install an HDMI splitter to connect your source and sink. In this way, the splitter provides a bypassed way to avoid HDCP errors so the signal would be transmitted successfully.
Final Thoughts
HDCP is a crucial technology in protecting digital content from unauthorized access and piracy. It plays an important role in protecting the rights of content owners. As digital content consumption continues to evolve, HDCP remains a fundamental component in preserving the integrity and security of copyrighted content.
FAQs
How do I know if my device supports HDCP?
Typically, you can identify HDCP support by the logo or message printed on the device. Or you can check the specification document of your device for confirmation.
What are some of the drawbacks of using HDCP?
To ensure uninterrupted HDCP content transmission, it's essential that all your devices and cables are HDCP-compliant. Failure to meet this requirement can result in HDCP errors, disrupting your content streaming experience.
Do I need HDCP 2.2 for a 1080p video from Netflix?
No, HDCP 1.4 is enough for 1080p. HDCP 2.2 supports a higher resolution of 4K if you need it.
Is HDCP 2.2 good for gaming?
If you need a 4K gaming screen and your device supports it, HDCP 2.2 is the way to go. But if your game console doesn’t support HDCP 2.x, HDCP 1.4 might be more suitable. For example, HDCP 2.2 is unnecessary for PS4 as the gaming console only supports 1080P.
For more information on this topic, you can keep up on our blogs. While VCELINK offers general and basic information for our customers and other visitors to the website, it’s not professional advice.






Be the first one to comment.
Leave a comment