Contents
Network cables play an important role in network installation and Internet connectivity. There are different types of Ethernet cables on the market and it’s important to choose the right Ethernet cable for your network infrastructure.
Ethernet cables can be classified according to categories and they can also be divided into shielded and unshielded ones. Unshielded Ethernet cables are generally referred to as “UTP” and shielded Ethernet cables are often abbreviated as “STP”. But in fact, it can be ambiguous as shielded network cables come in various types. We’ll discuss shielded vs unshielded Ethernet cable in this blog and give you a more clear guide.
What is Unshielded Ethernet Cable?
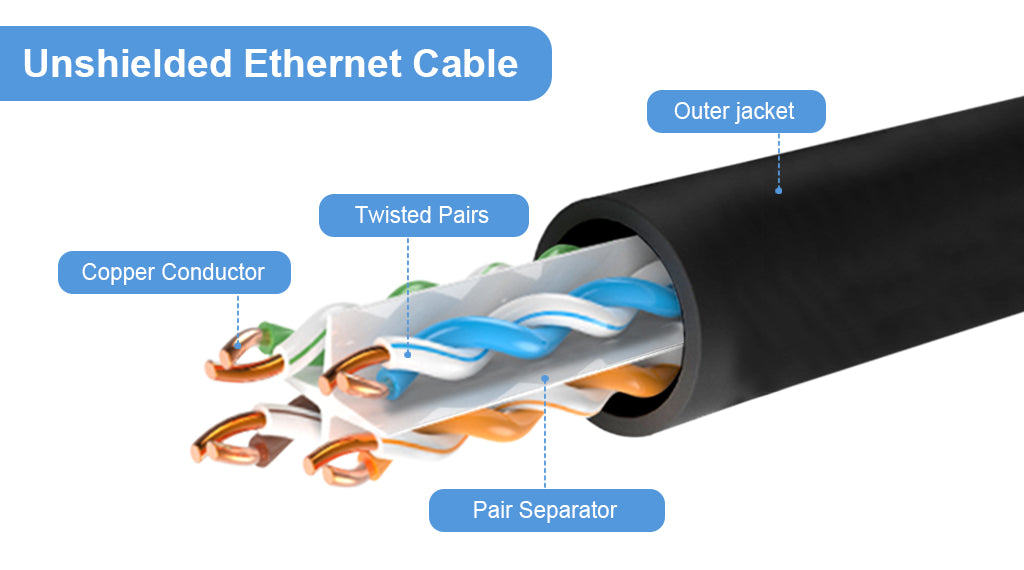
People often refer to an unshielded Ethernet cable as UTP. These Ethernet cables have no extra insulation covering and provide less EMI protection. But they have the same bandwidth, speed, and maximum distance as shielded cables in the same category. Unshielded Ethernet cables are susceptible to interference from electrical equipment and exterior influence such as temperature and water. So these network cables are often used in indoor applications such as homes and offices.
What is a Shielded Ethernet Cable?
The need for speed in the network drives the new development of cabling technology and shield twisted cables have become commonly used in high-speed networks. Shielded Ethernet cables are designed to protect from Electromagnetic Interference (EMI). Shielded Ethernet cables help protect wire through different constructions including braided and foil shielding. Compared to unshielded cables, shielded Ethernet cables helps reduce electromagnetic interference and radio frequency interference. So they are often used in applications where EMI and RFI are big problems. Shielded Ethernet cables are referred to as “STP”, but it can be confusing and there are different shielding types.

Ethernet Cable Shielding Types
Shielded Ethernet cables usually feature a shielding for the entire cable or separated twisted pairs. There are different Ethernet cable shielding types including F/UTP, U/FTP, S/UTP, SF/UTP, F/FTP, S/FTP, and SF/FTP.
- F/UTP ( Foiled With Unshielded Twisted Pairs): A shielded Ethernet cable features an overall foil shielding with four unshielded twisted pairs. This type of shielded Ethernet cable offers basic protection from EMI/RFI.

- U/FTP (Unshielded With Foiled Twisted Pairs): This Ethernet cable has no overall shielding, but each twisted pair is wrapped by a foil shielding, which can offer some protection from EMI and reduce crosstalk.

- S/UTP (Shielded With Unshielded Twisted Pairs): A shielded Ethernet cable that usually uses a braid or foil screen around the entire cable. But the twisted pairs are unshielded. This type of cable is often abbreviated as STP. This type of cable is common and traditional, but the braided shielding can add extra weight to the cable.

- SF/UTP (Shielded and Foiled With Unshielded Twisted Pairs): A shielded Ethernet cable that has both the braid and foil overall shielding with four unshielded twisted pairs. This combination of shielding can effectively protect against EMI and reduces crosstalk between internal wires.

- F/FTP (Foiled With Foiled Twisted Pairs): This type of network has four twisted pairs with a foiled shielding and the entire cable is also wrapped into a foil shield. This cable construction provides great protection against EMI and RFI and reduce crosstalk between adjacent wires.

- S/FTP (Shielded With Foiled Twisted Pairs): A shielded cable that has an overall strong braid screen and foil shield around each twisted pair. This is a very common shielded Ethernet cable as it can provide 100% protection with durability and flexibility.

- SF/FTP (Shielded and Foiled With Foiled Twisted Pairs): This cable has both foiled and braid screen with foil-shielded twisted pairs. It helps provide maximum protection from EMI and RFI. Currently, this shielded cable has had the highest level of shielding, which is also future-proof.

Unshielded vs. Shielded Twisted Pair Cable
People understand that unshielded and shielded cables are different, but in fact, they also have many similarities. For example, in the same category, unshielded and shielded cables share the same bandwidth and speed. Let's get down to the differences and similarities between shielded and unshielded cables.
Similarities
- Often paired with RJ45 connectors and keystone jacks
- Terminated with the same network tools such as RJ45 crimping tools and punch down tools
- Support the same speed and bandwidth in the same category ( e.g. both shielded Cat6 cable and unshielded Cat6 cable can support the maximum bandwidth of 250 MHz and speed of 10 Gbps over a short distance of 37-55 meters)
- Can be terminated according to T568A or T568B wiring standards based on your own need
Differences
- Shielded Ethernet cables provide greater protection against EMI and RFI for a more stable data transmission
- Shielded Ethernet cables are often more expensive than unshielded cables
- The installation of shielded Ethernet cables can be a bit more difficult than that of unshielded ones
- Shielded cables should be paired with shielded hardware for maximum performance and that shielded hardware is more expensive
Which Ethernet Cables Do I Need?
Will shielded Ethernet cables always be the best solution for your network installation? Not really. There are many factors that you should consider including the scenarios, costs, and installations.
Shielded Ethernet cables do perform better in the protection against EMI and RFI, but they are more expensive than unshielded cables. In addition, shielded Ethernet cables are usually thicker and heavier due to their shielded construction, making the installation more difficult.
So which cable should you use? Make sure where the cable will be installed. If your network is located in a place with lots of electronic devices or close to high-voltage equipment, don’t hesitate to get shielded cables. And if you’re concerned about the stability and flexibility of data transmission, just get shielded cables. In addition, if you want to install cables outdoors, the shielded Ethernet cable is your prior option.
In other conditions, if you don’t want to spend too much on the cable, just get an unshielded Ethernet cable for your home and office network. But make sure that you buy the high-standard unshielded cable.
For more information on this topic, you can keep up on our blogs. While VCELINK offers general and basic information for our customers and other visitors to the website, it’s not professional advice.






Be the first one to comment.
Leave a comment