Contents
There are mainly three types of cables used in network connection: twisted pair cables, coaxial cables, and fiber optic cables. Among them, fiber optic cables have become more and more popular in recent years for their information carrying at a high speed and it may gradually replace copper wires in the future.
What is a Fiber Optic Cable?
Fiber optic cable, also known as optical fiber cable, is designed to meet different needs of optical or mechanical environments. It contains various strands of optical fiber in an insulated casing that is used to transmit light. A fiber optic cable performs well in long-distance data transmission and telecommunications. A fiber optic cable can have many strands of fibers and each strand is as thin as human hair, but these thin fibers are very powerful. They can carry a large amount of information and transmit data at a high speed.
Optical Fiber Structure
The simplest fiber optic cable is generally composed of four parts: core, cladding, coating, strength member, and jacket.
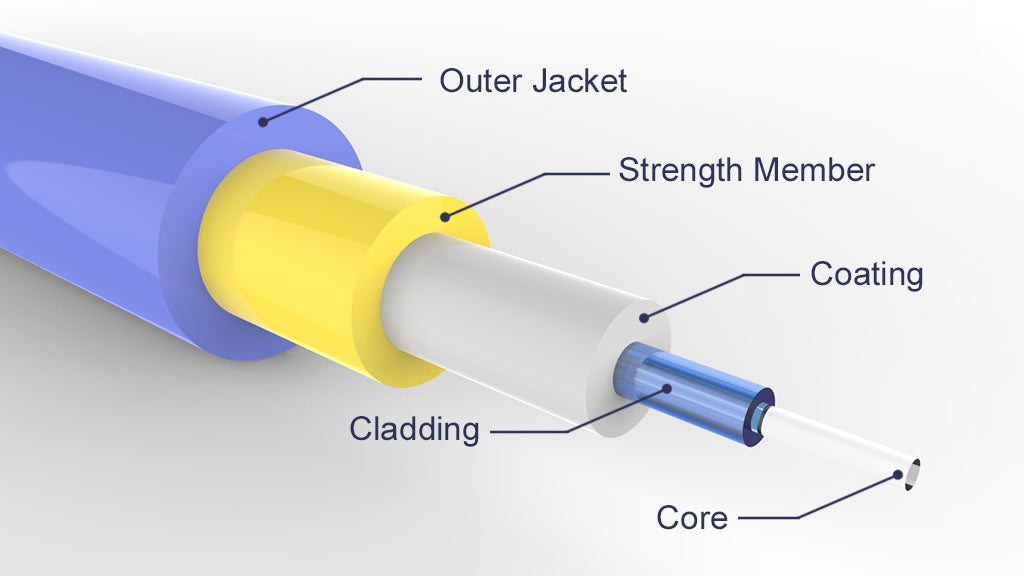
A fiber optic cable features a core in the center, which is designed to transport light. The cladding is a thin layer that helps transmit data through the fiber. There is also a coating over the cladding to give further protection for the fiber core. The strength member, also known as strengthening fibers, is usually made of steel, fiberglass, or aramid yarn to keep the fiber core from damage, especially during the installation. The exterior part of the fiber optic cable is called the cable jacket, which is designed to protect the cable from environmental damage.
In addition, the outer jacket is often color-coded to identify the type of fiber optic cable. This is the basic structure of fiber optic cable, but it can feature different structures according to different types.
Types of Optical Fiber Cables
Optical fiber cables can be divided into different types according to different structures, materials, applications, and transmission methods.
Single Mode vs Multimode Fiber
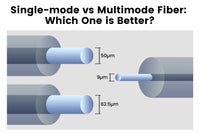
Single-mode fiber (SMF), also known as fundamental or mono-mode fiber, features only one transmission mode as it has a relatively small diametral core. Multimode fiber features a large diametral core that allows multiple modes of light to pass through.

Compared to single-mode fiber, multimode fiber is more cost-effective and suitable for a short distance such as data transmission in LANs. Single-mode fiber has less light reflection when the light passes through the core, so it allows the signal to go further. Single-mode fiber is greater for long-distance applications such as colleges and even the submarine network.
Single-mode fiber can often be divided into OS1 and OS2, while multimode fiber is usually classified into OM1, OM2, OM3, OM4, and OM5. There are different color codes for different kinds of optic fibers, and you can refer to the following chart.

Indoor Fiber Optic Cable vs Outdoor Fiber Optic Cable
Indoor Fiber Optic Cable
The production process of indoor fiber optic cables can be simpler than outdoor fiber optic cables. It is usually composed of a fiber core, protective sleeve, and sheath. Indoor fiber optic cable features low mechanical stress and the protective layer is not strong enough, but it is lighter and more cost-effective than outdoor fiber optic cables. Indoor fiber optic cables can be often seen in the buildings and homes. The key feature of indoor fiber optic cable is fire resistance.

Outdoor Fiber Optic Cable
There are different types of outdoor fiber optic cables including underground fiber cables, direct burial fiber cables, aerial fiber cables, and submarine fiber cables. Outdoor fiber optic cables can be easily affected by external environments and they should be more robust than indoor fiber optic cables. We’ll give a brief introduction to outdoor fiber optic cable in this article.

- Aerial Fiber Optic Cables: Aerial fiber optic cables can often be seen hanging on the poles or buildings. They are usually exposed to extreme environments such as wind, ice, and storm, so it can be easier to damage than direct burial fiber cables and pipe fiber optic cables. Aerial fiber optic cables are often divided into two types: self-supporting and catenary wire.
- Direct Burial Fiber Cables: Direct burial fiber cables are buried underground, usually 0.8 to 1.2 meters deep. These cables should be resistant to dust, soil erosion, and animal chewing.
- Pipe Fiber Optic Cables: Pipe fiber optic cables are usually installed in cities. The pipe usually features a good environment, so it has no special requirement for pipe fiber optic cables.
- Underwater Fiber Optic Cables: Underwater fiber optic cables should withstand harsh environments, so they are generally made with a gel or powder. They should also feature excellent resistance to water and moisture. It has even higher requirements for submarine fiber optic cables and they should have at least 25 years of lifespan.
Tight Buffered vs Loose Tube
According to the construction of optic fiber cables, they can be divided into tight buffered and loose tube cables.
Tight buffered cables are usually made with 900μm buffered fibers. The fiber core is surrounded by aramid yarn or glass strength members in an outer jacket. The tight buffer inside the cable is used to protect the fiber from damage, especially during the installation. Tight buffered cables are often used in buildings or universities.
Loose tube fiber optic cables feature 250μm fibers in gel-filled loose tubes. Such kind of loose tube cables usually features a central member to offer stability. Loose tube fiber optic cables are more suitable for harsh outdoor environments as the gel-filled protective layer protects the cable from water and extreme weather.
Final Thoughts
A thin optical fiber can transmit information from one place to another and fiber has an advantage over copper wires for its high bandwidth, long distance, and no interference. So, fiber optic cables have been widely used in different applications in recent years.
To meet the different needs of fiber cable installations, there are various fiber optic cables on the market. And if you have special requirements, you can also customize one from the manufacturer according to your own need.
For more information on this topic, you can keep up on our blogs. While VCELINK offers general and basic information for our customers and other visitors to the website, it’s not professional advice.


Be the first one to comment.
Leave a comment