Contents
Ethernet can be carried by many different cables, including fiber optic cables, coaxial cables, and twisted pair cables (also known as Ethernet cables). Bulk Ethernet and coaxial cables can transfer the data signal over the Ethernet network. Both of them contain copper, but they are very different from each other. How do these cables differ from each other when they are used as network cables?
What is Coaxial Cable?
Invented by Oliver Heaviside, coaxial cables were first used in the 1880s. They are electrical cables that contain a conductor surrounded by copper shielding, and they share the same geometric axis. A coaxial cable is usually composed of four main parts: the central copper conductor, the dielectric insulation, the woven copper shielding, and the outer cable jacket. The advantage of coaxial cables is that they can restrict the signal inside the dielectric, which can keep the cable from outside interference.

What are coaxial cables used for? Coaxial cables are often used for video, audio, and data transmission. They can often be found in cable televisions, high-frequency antenna installations, satellite antenna installations, and broadband Internet networks. Nowadays, when people refer to Ethernet cables, they are talking about twisted pair cables. But in fact, coaxial cables have been used in 10BASE5 Ethernet.
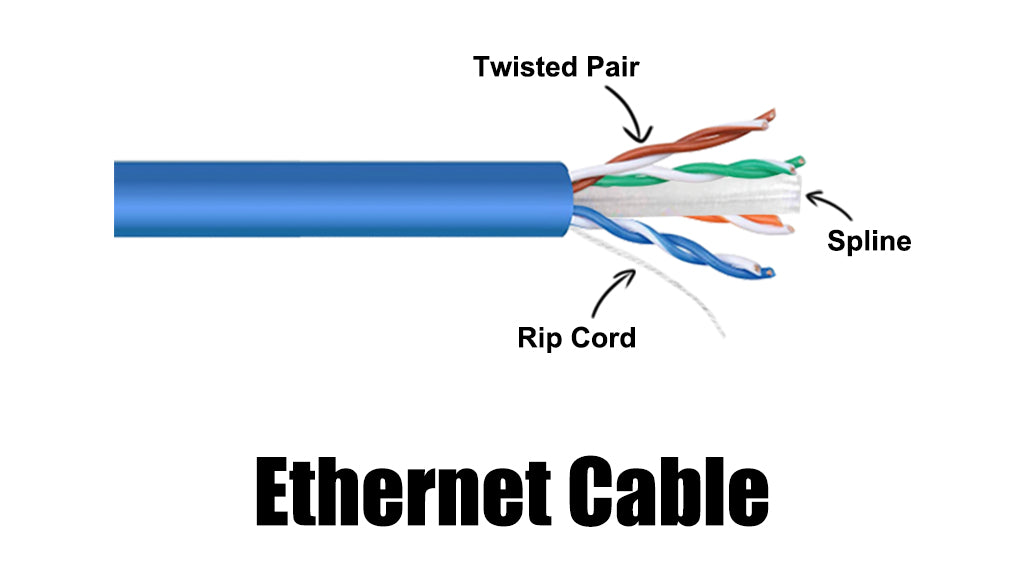
What is Ethernet Cable?
People may be more familiar with twisted pair cables, commonly referred to as Ethernet cables, LAN cables, or network cables. The Ethernet cable features four twisted pairs of copper wires shielded by a jacket. Unlike the coaxial cable, eight conductors don’t share the same axis. They can be divided into shielded and unshielded types, and these cables can also be classified into different categories, including CAT5E, CAT6, CAT6A, CAT7, and CAT8.
Twisted pair cables are commonly used in Local Area Network (LAN). The twisted pairs are designed to reduce crosstalk and avoid noise and electromagnetic interference (EMI). Know more about Ethernet cables from Ethernet cable 101.
Comparison: Coaxial vs. Ethernet
So, what are the differences between coaxial and Ethernet cables? Do Ethernet cables perform better than coaxial cables? Can you use a coaxial cable instead of an Ethernet? Which one should I choose? You can find the answer in this article.
Length
It is known that the maximum distance of Ethernet is 100 meters (328 feet) using twisted pair cables. If the cable exceeds the distance of 100 meters, the network speed will be affected. A coaxial cable can be installed over a longer distance than an Ethernet cable with less signal loss. (The maximum length of a coaxial cable is 500 meters or 1640 feet.)
Speed
The Ethernet cable is definitely the winner when it comes to Internet speed. You know that different categories of Ethernet cables have different speeds and bandwidths. But even the older version of CAT5 cable can transmit data at 100 Mbps, and the maximum bandwidth can reach 100 MHz. So, what’s the transmission speed of the coaxial cable? The speed of the coaxial cable is 10 Mbps, which is much slower than the twisted pair cable.
Applications
Twisted pair cables are commonly used in local area network, and they are an essential part of home networks, office networks, and data centers. These cables are paired with RJ45 connectors, and they can work with any device that has Ethernet ports. Coaxial cables are the dominant cables for connecting televisions to antennas, and they can also help transmit CATV, HDTV, and CCTV signals. They were used for long-distance telephone networks but have been gradually replaced by optic cables and twisted pair cables.
Installation
Because of their bulky size, coaxial cables are more complex and costly to install than twisted pair cables. Twisted pair cables are more flexible and thinner so that they can be bent even in a tight place, and they are also easy to install even if you’re a novice.
Coaxial vs. Ethernet Cables: Which to Choose?
Whether to use coaxial or Ethernet cables depends on your own needs.
Choose coaxial cables for cable TVs or connecting the receivers to antennas. For example, they are great for signal distribution of CATV, CCTV, and HDTV, and they can also be used in digital audio applications (known as S/PDIF). Coaxial cables can be classified into RG6, RG7, RG8, RG9, RG11, RG59, RG60, etc., among which RG6, RG11, and RG59 are the most common types. RG6 and RG59 are used for TV, and RG11 can be an advanced version applied at a longer distance.

Don’t hesitate to get twisted pair cables to build an Internet connection. Cat5e and Cat6 cables are often used for home or office networks, while Cat6a and Cat8 network cables are applied in server rooms or data centers. Ethernet cables are also suitable for PoE applications such as IP cameras and VoIP phones.

Tips: People often refer to twisted pair cables as Ethernet cables because most use them for their home or office network. But in fact Ethernet cables include coaxial, twisted pair, and fiber optic cables.
For more information on this topic, you can keep up on our blogs. While VCELINK offers general and basic information for our customers and other visitors to the website, it’s not professional advice.






“Great comparison between coaxial and Ethernet cables! Understanding the pros and cons of each is crucial for anyone setting up a network. The clarity in highlighting the differences and use cases helps readers make informed decisions. Personally, I appreciate the emphasis on performance and reliability. This post is a valuable resource for those looking to optimize their network infrastructure. Thanks for breaking down the complexities in a concise and accessible manner!”