Contents
Fiber optic cables provide faster speed and are superior to regular cables like copper and coaxial cable. These cables are widely applied in telecommunications, data centers, and industry automation. Fiber optic cables can be divided into different types based on their constructions, designs, and applications. Simplex and duplex fiber patch cables are often seen on the market and do you know what they are? Understanding the distinctions between simplex and duplex cables is crucial for anyone who is often involved in the installation and maintenance of fiber networks.
What is Simplex Fiber Optic Cable?
The simplex fiber optic cable only features a single plastic fiber protected by a jacket, and it can only transmit in a single direction at a time. For instance, the radio station can transmit signals to audiences, but cannot receive feedback from the audiences. Simplex fiber optic cables are compatible with different fiber connectors, such as SC and LC connectors based on different applications. These cables are available in different lengths to meet various requirements.
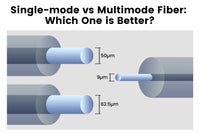
There are single-mode and multimode simplex fiber optic cables with different characteristics. Single mode simplex cables typically feature a core diameter of 8 to 10 micrometers, suitable for those applications that require a high-speed network over long distances without signal loss. Multimode simplex cables have a larger diameter of about 50 and 62.5 micrometers, which has a lower bandwidth and speed.
Simplex fiber optic cables are easy to install and maintain due to their single fiber. It also offers resistance to external interference. However, with their unidirectional transmission, they may have restricted bandwidth.
What is Duplex Fiber Optic Cable?
“Duplex” includes the meaning of “two” in Latin. It consists of two strands of fibers, each with its own core, cladding, and protective layer. Duplex cables contain two plastic fibers with a zipper construction, so they can support a bidirectional transmission without mutual interference.

Types of Duplex Fiber Optic Cable
Does the bidirectional transmission always happen at the same time in duplex cables? It depends on the type. Here is the detailed information on two duplex fiber optic cables: half-duplex and full-duplex.
- Half-duplex:Half-duplex communication allows for two-direction data transmission but it only supports one-direction transmission at a time. A common example of half-duplex data transmission is the walkie-talkie. Two people on two ends of a walkie-talkie cannot speak at the same time, instead, one person speaks while the other listens. Half-duplex transmission can sometimes be inefficient for communication.
- Full-duplex: Full-duplex supports simultaneous bidirectional transmission. Both ends can transmit and receive signals at the same time. Full-duplex communication is like a two-way highway where traffic flows in both directions at the same time. The other common example of full-duplex is a phone call and two persons at two ends of the phone can hear and speak to each other at the same time. Besides, full-duplex provides enhanced data speeds, resulting in efficient communication.
Duplex fiber optic cables can be more complex to install and maintain with their two fibers, but they can achieve a high data transmission speed. In addition, if duplex cables are not properly shielded or separated, crosstalk can occur.

Simplex vs. Duplex: What are the Differences?
To give you a better understanding of the differences between simplex and duplex fiber optic cables, the following comparison chart offers a detailed comparison.
|
Simplex Fiber Optic Cable |
Duplex Fiber Optic Cable |
|
|
Strands of Fiber |
1 strand of fiber |
2 strands of fibers |
|
Signal Direction |
One-direction transmission from transmitter to receiver |
Two-way direction transmission |
|
Fiber Arrangement |
A single plastic fiber inside the protective layer |
Two plastic fiber with zipper constructions |
|
Speed |
Simplex<Duplex |
|
|
Cost |
Simplex<Duplex |
|
|
Performance |
Simplex<Duplex |
|
|
Installation |
Easy |
Complex |
Simplex vs. Duplex Applications
Simplex and duplex fiber optic cables are commonly used in different applications in the form of fiber optic pigtails or fiber patch cords. Here are some of their common usages.
Applications of Simplex Fiber Optic Cables
Simplex fiber optic cables are mostly used in applications that require single-direction transmission such as broadcasting and sensor systems. Typically, data will be transmitted from the source to the receiver.
In television broadcasting, simplex fiber optic cables will transmit data from the camera to the stations. Simplex fiber optic cables can transmit data to audiences but cannot receive signals from them. In sensor systems, particularly in the Internet of Things (IoT), signals are usually sent from the sensor to the control or monitoring station. Simplex fiber optic cables are widely used in the monitoring system like CCTV cameras. These cables also play a crucial role in the medical field.
Though simplex fiber patch cables are suitable for a wide range of applications, they cannot be for some usage like biometric authentication because face or fingerprint recognition requires bidirectional communications.
Applications of Duplex Fiber Optic Cables
Duplex fiber optic cables are the backbone of modern LAN and WAN applications. With the help of duplex fiber optic cables, these systems will get a high-speed bidirectional transmission with low latency and signal loss.
In LAN environments, duplex fiber optic cables are often used with routers, switches, and fiber servers to enhance network performance. For example, duplex fiber optic cables are laid on the ocean floor, connecting the whole world. These fibers are also well suited for VoIP calls, providing efficient communication with less latency.
In general, both simplex and duplex fiber optic cables have their own advantages and respective fields.
Conclusion
Simplex and duplex fibers have different features and applications. Simplex fiber optic cables are easy to install and often used in one-way data transmission. Duplex fiber optic cables boast superior performance like higher data speed and bandwidth, making them ideal for bidirectional data transmission. They have their own pros and cons and the selection between the two depends on your specific requirements and network demands.
For more information on this topic, you can keep up on our blogs. While VCELINK offers general and basic information for our customers and other visitors to the website, it’s not professional advice.


Be the first one to comment.
Leave a comment